Our world depends on technology to communicate and propel productivity in every industry, including manufacturing.
Thanks to this technology, and to advances in automated systems and programming, our manufacturing processes are cleaner, more efficient, and more accurate than ever before.
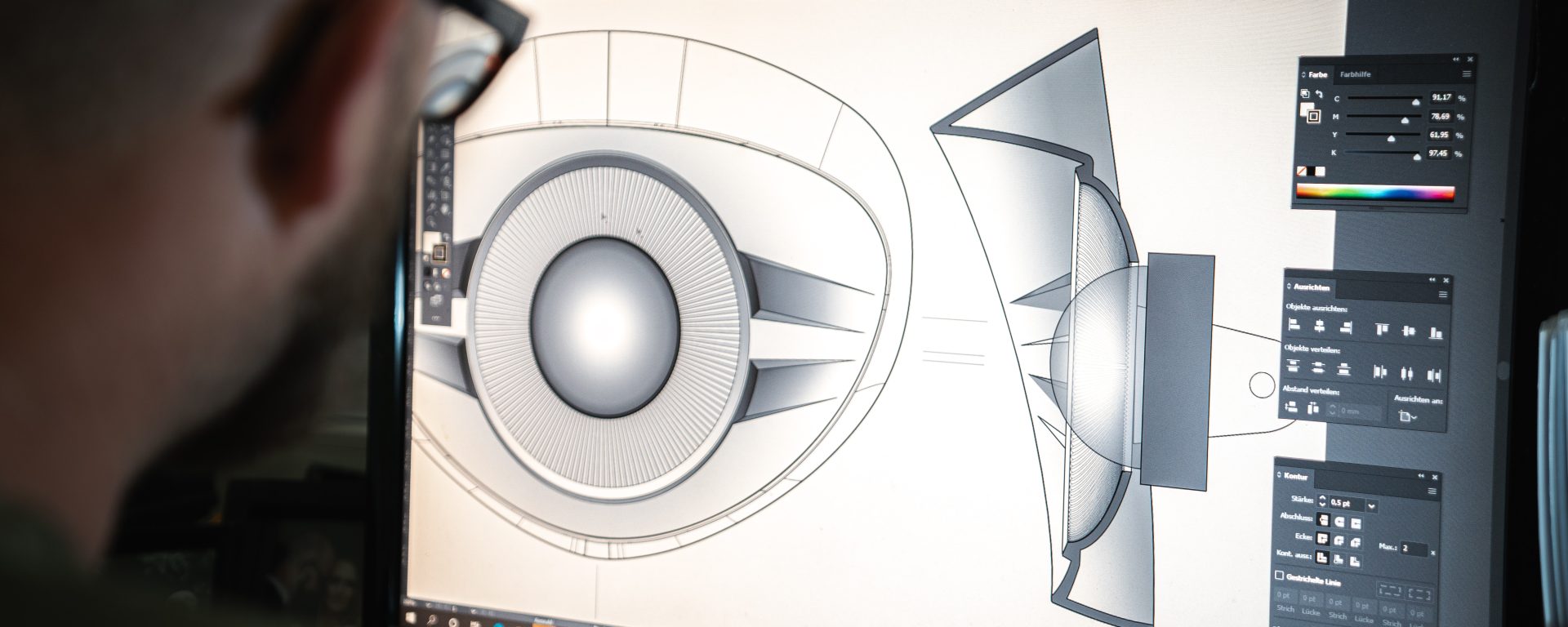
For example, the implementation of computer-aided manufacturing, including computer-aided design (CAD) and computerized numerical control (CNC), has streamlined manufacturing as we know it. Computer-aided manufacturing has eased and elevated processes, turning initial ideas into two-dimensional and three-dimensional model designs.
This article will define computer-aided manufacturing, describe how it is utilized in the manufacturing industry, and show why it’s important and vital to modern manufacturing today.
What is Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM)?
Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) is the use of software and computer-controlled machinery to automate a manufacturing process. As its name implies, CAM does this by controlling machine tools in the production of goods.
CAM software also plans, manages, and controls the manufacturing plant’s operations through direct or indirect computer interfaces, along with the plant’s production resources.
Two examples of the processes and programs utilized in computer-aided manufacturing include both computer-aided design (CAD) and computerized numerical control (CNC).
- Computer-aided design (CAD): A manufacturing process that enables manufacturers to digitally create 2D drawings or 3D models of future products. This process helps designers and engineers alike visualize a product’s construction before creating it by using computers to develop, modify, and optimize the design. In turn, the designs created are more detailed, accurate, and efficient representations of the manufactured products.
- Computerized numerical control (CNC): This computerized manufacturing process uses pre-programmed software and code to control the movement of production equipment. Machinists can control a variety of complex machinery, including grinders, lathes, and turning mills, to cut, shape, and create different parts and prototypes.
Interested in becoming a CNC Machinist? Check out our downloadable CNC Machining Get Started Guide to learn more about Goodwin’s CNC program offerings, curriculums, and more!
How is Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) Utilized in the Manufacturing Industry?
Computer-aided manufacturing and machinery have changed manufacturing as we know it by streamlining the design of products, contributing to higher-quality goods, and allowing manufacturing teams to collaborate and communicate on designs more easily.
Examples of other computer-aided manufacturing used today are:
- Additive practices, such as 3-D printing and prototyping equipment, reduce lead times and simplify the concept of the creation process.
- Advanced data analytics detect early defects, improve process control, and provide avenues for preventative maintenance.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) and robotic automation reduce costs by performing repetitive tasks.
- Material extraction equipment like drills, saws, and laser cutters can easily adjust manufacturing specifications.
Not only are the types of manufacturing processes varied, but so too are the industries and fields that utilize computer-aided manufacturing.
The fields of electrical engineering, industrial engineering, structural engineering, architecture, interior design, aeronautics, automotive design, plumbing design, construction, and even medical and dental device manufacturing all use this incredibly useful technology.
Why is Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) Important?
The technology behind computer-aided manufacturing has innovated and enhanced industrial development and provided sustainable solutions for companies and consumers alike.
By digitizing the manufacturing process, companies are able to streamline accounting processes, inventory control, and supply chain management, as well as enact computerized functions in factories, ensuring production is ongoing and continuous.
Additionally, by implementing computer-aided design (CAD) technology, engineers, architects, and other manufacturing professionals can expedite the most important and crucial technical drawing stage, allowing them to produce easily understood and professional-looking designs faster.
Here are five more reasons why computer-aided manufacturing and machinery is important to modern manufacturing:
1. Advanced adaptability. This technology allows us to use simulations to scale projects quickly, add value to societal norms, and achieve optimum solutions when problems do arise.
2. Analyzes present-day issues. Advances in technology allow us to address pressing issues like carbon emissions, climate change, and advancing medicine as well as aging population needs.
3. Enhances evidence-based research and product development. By automating repetitive tasks, like symbol placements and drawing storage, manufacturing technology reduces error, prevents common design mistakes, and even forecasts potential errors throughout the design process.
4. Optimizes output production. Custom-made, cost-effective goods are created and able to get to the market faster.
5. Strengthens health and safety. Human hazard decreases due to the automated technology performing most of the labor.
Start Your Computer-Aided Manufacturing Career Today
Now that we’ve defined and explained computer-aided manufacturing and highlighted the importance of this technology in the manufacturing industry, it should come as no surprise why many individuals pursue careers as drafters, technicians, and operators.
Plus, with more postsecondary education available through convenient and career-focused training programs, students can pursue a manufacturing career they love faster than ever before.
Every college and university will offer different manufacturing training programs so students should do their research. At Goodwin University, we offer both an Associate and Certificate in Computer Numerical Control (CNC) Machining, a Certificate in Computer Numerical Control (CNC) Machining, Metrology, and Manufacturing Technology, as well as an 18-credit Computer-Aided Design (CAD) certificate.
All of these programs are career-focused and provide customizable scheduling options, a comprehensive curriculum, and the practical, hands-on experience students need for their future manufacturing careers.
Find out more information about our manufacturing programs, field-expert faculty, state-of-the-art facilities, and flexible class offerings by contacting us today.
Let’s crush your career goals – together!
Goodwin University is a nonprofit institution of higher education and is accredited by the New England Commission of Higher Education (NECHE), formerly known as the New England Association of Schools and Colleges (NEASC). Goodwin University was founded in 1999, with the goal of serving a diverse student population with career-focused degree programs that lead to strong employment outcomes.